What Organelle Does Pompe Disease Affect In The Cell
What organelle does pompe disease affect in the cell. Pompe disease causes muscle weakness and trouble breathing. It is the only glycogen storage disease with a defect in lysosomal metabolism and the first glycogen storage disease to be identified in 1932 by the Dutch pathologist JCPompeThe build-up of. Alzheimers disease affects brain cells known as neurons in specific regions of the brain that are involved in memory and thinking.
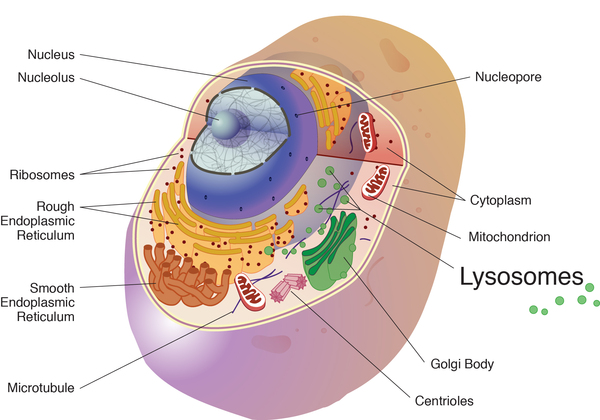
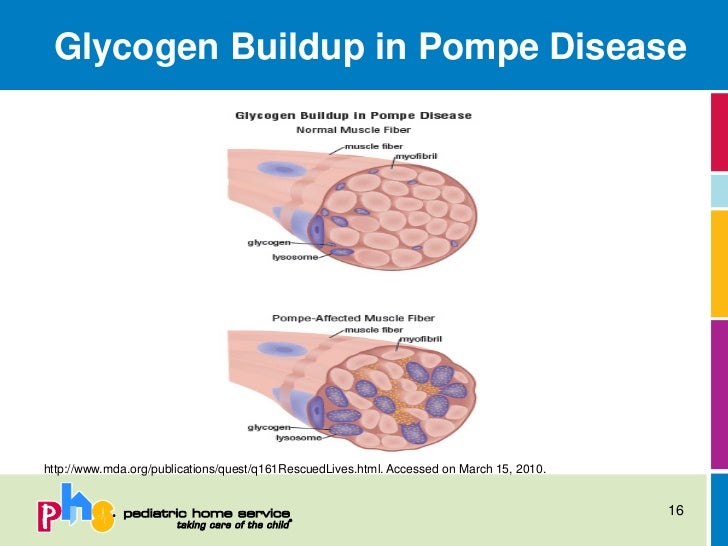
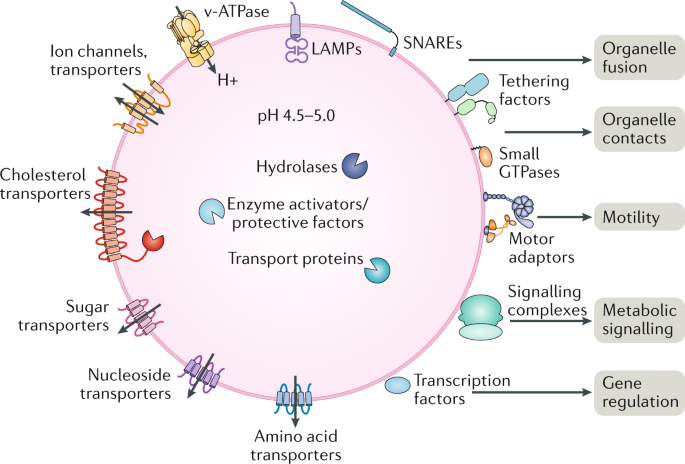
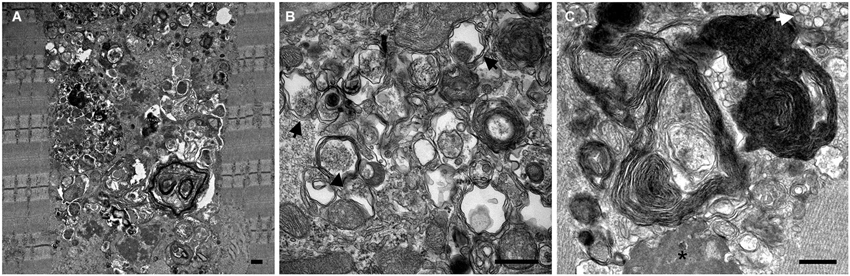
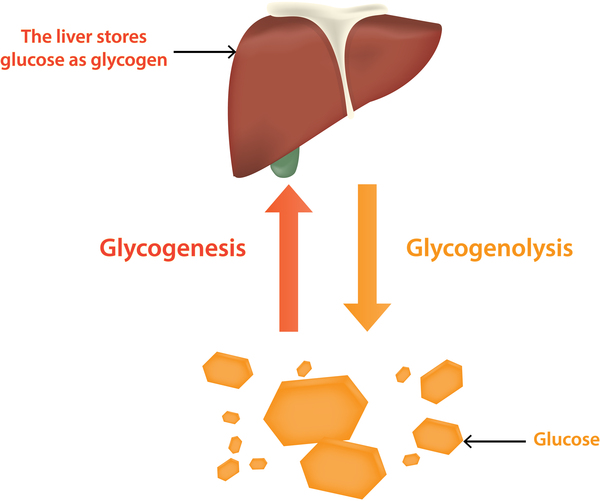
Too much sugar builds up and damages your muscles and organs. Other cells in the brain are thought to have roles in the disease process as well including specialised immune cells called microglia. Pompe disease is a lysosomal storage disorder where glycogen accumulates in cell structures called lysosomes bags of about 50 different enzymes surrounded by a membrane similar to the cell membrane which function as the digestive system for the cell.
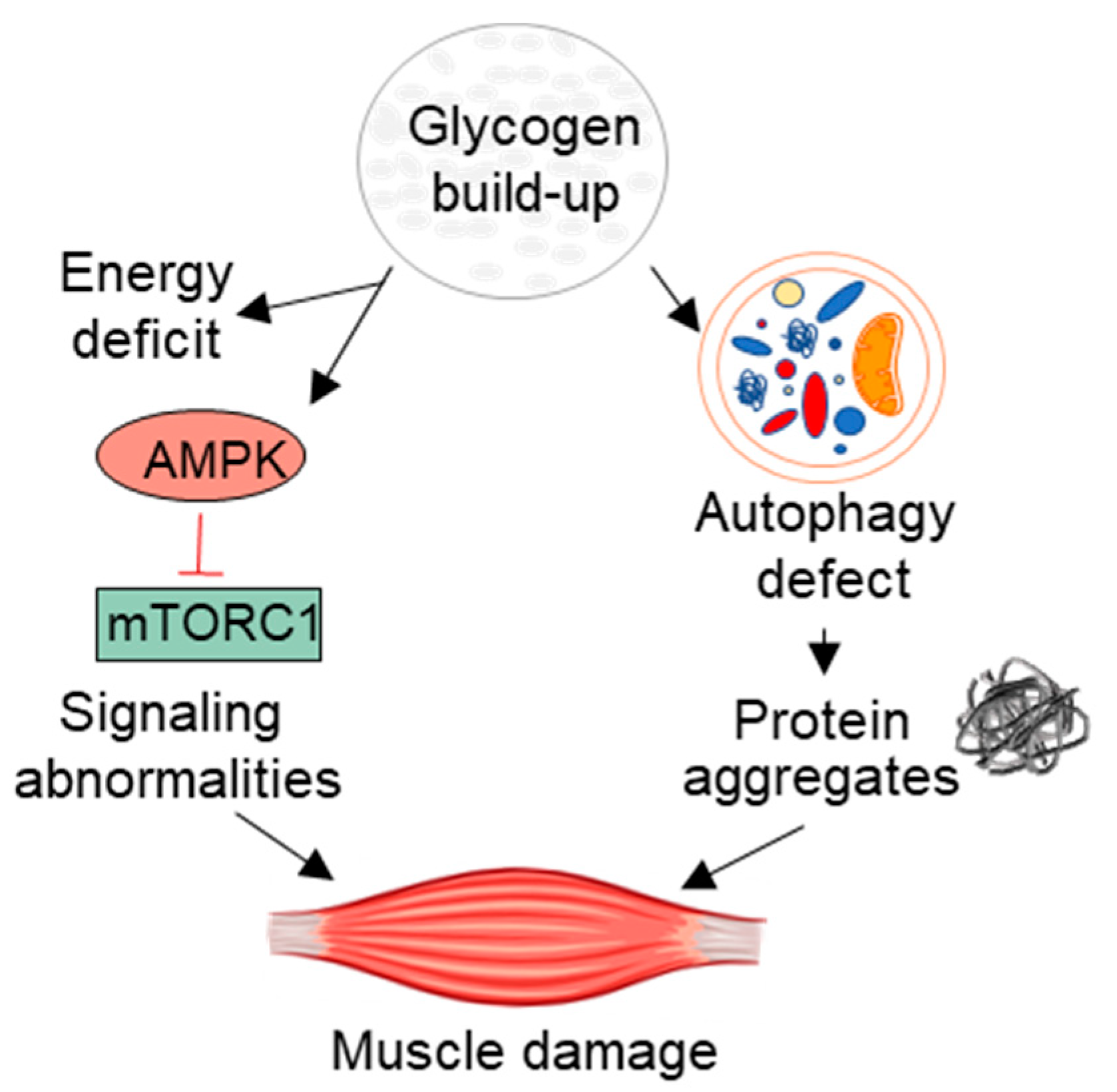
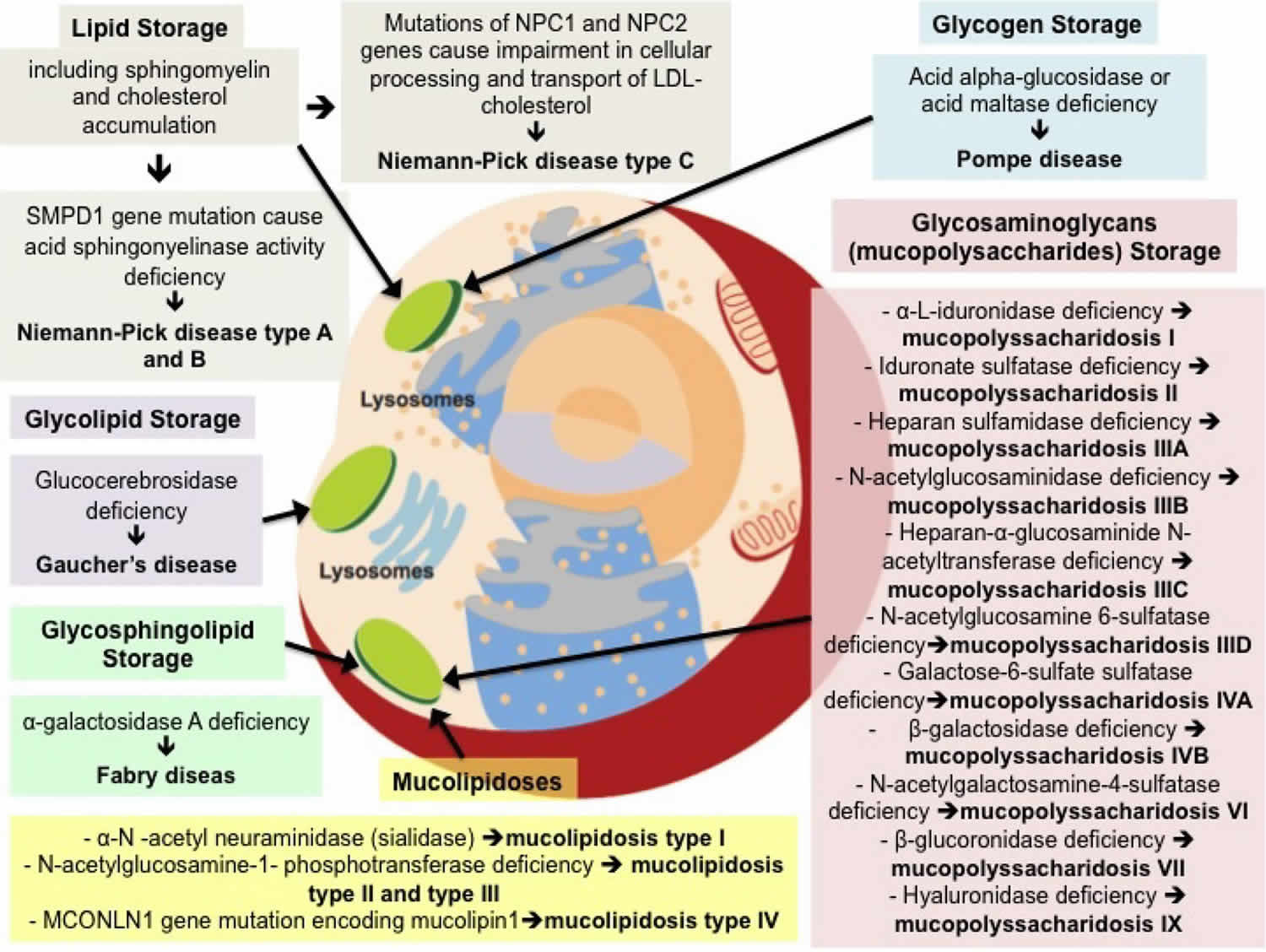
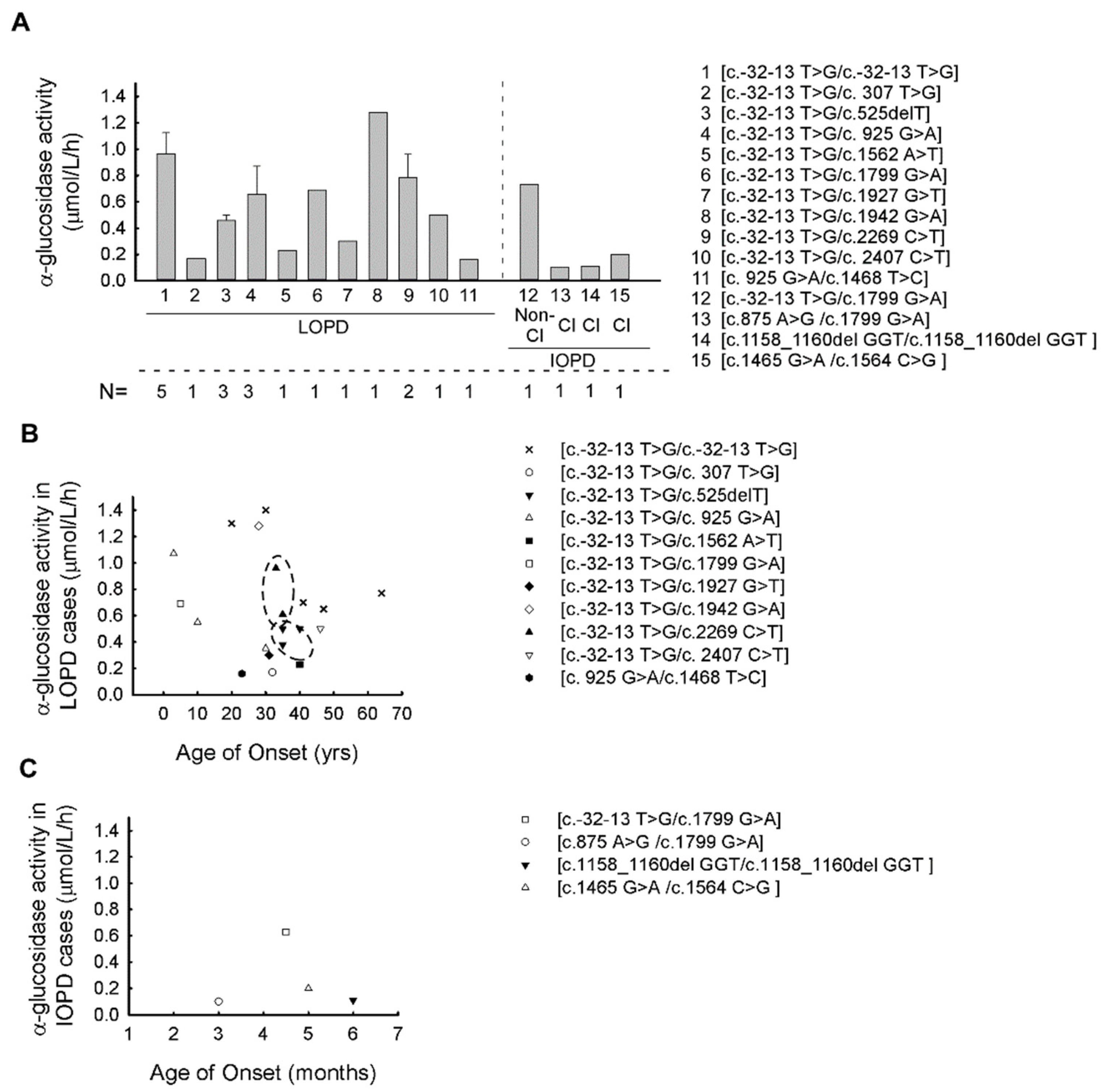
It is caused by an accumulation of glycogen in the lysosome due to deficiency of the lysosomal acid alpha-glucosidase enzyme. Pompe disease is a rare genetic condition that causes an abnormal buildup of glycogen a sugar molecule inside your cells. Pompe Disease damages muscle and nerve cells throughout the body.
The defect results in a build-up of glycogen in the lysosome a saclike storage organelle in the cell that acts as a waste-disposal system leading to. The most commonly affected body areas are the heart respiratory system and skeletal muscles. α14-Glucosidase deficiency a lysosomal storage disorder is one of the causes of Pompe disease.
When a child inherits a pair of altered genes from 2 parents who are carriers as described above the result is decreased or absent levels of the GAA enzyme. One may also ask is. Pompe disease is a rare autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in an enzyme that degrades glycogen.
Pompe disease can lead to weakness and breathing problems. Autosomal recessive disorders are genetic diseases which occur only when a. The disease results from the deficiency of an enzyme called acid alfa glucosidase GAA which breaks downs complex sugars in the body.
Pompe disease is an inherited disorder caused by the buildup of a complex sugar called glycogen in the bodys cells. How Does Pompe Disease Affect the Muscles.
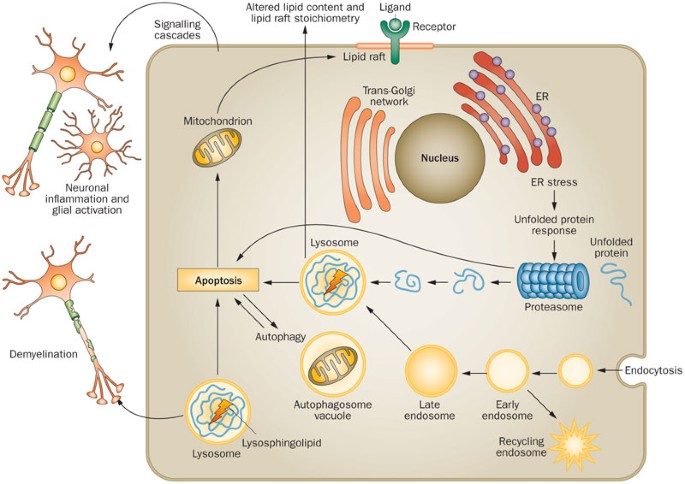
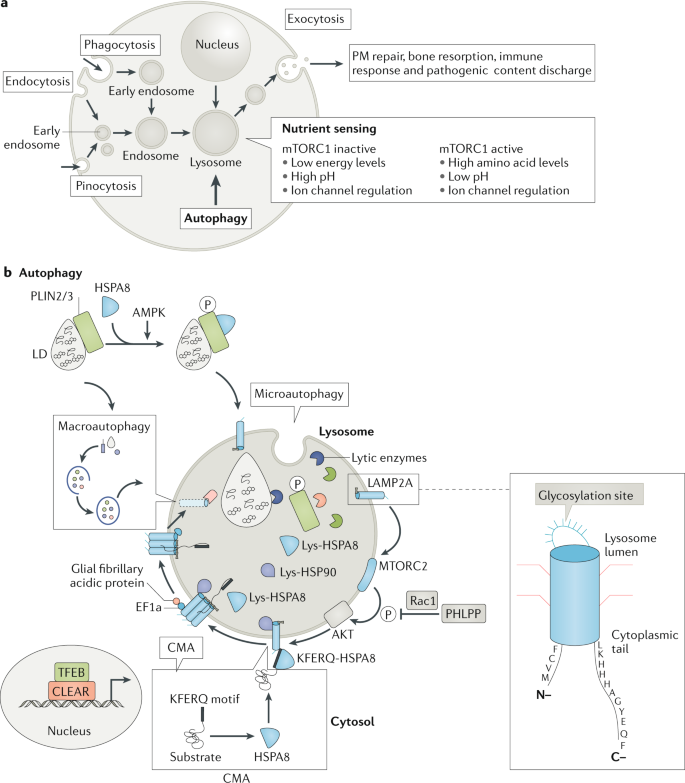
Lysosomes and Pompe Disease Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles containing hydrolytic enzymes that break down cellular debris.
Other cells in the brain are thought to have roles in the disease process as well including specialised immune cells called microglia. Pompe disease causes muscle weakness and trouble breathing. Lysosomes and Pompe Disease Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles containing hydrolytic enzymes that break down cellular debris. Pompe disease is a rare autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in an enzyme that degrades glycogen. It mostly affects the liver heart and muscles. The GAA gene is responsible for making this enzyme. Pompe Disease damages muscle and nerve cells throughout the body. When a child inherits a pair of altered genes from 2 parents who are carriers as described above the result is decreased or absent levels of the GAA enzyme. The major cell type affected by glucosylceramide storage in this disease is the macrophage Gaucher cells whose dysfunction affects the production and turnover of cells belonging to the hematopoietic system.
The GAA gene is responsible for making this enzyme. 15 What organelle does Pompe Disease affect in the cell and how does this disease affect someones life. This buildup occurs in organs and tissues especially in muscles causing them to break down. Pompe disease is an inherited disorder caused by the buildup of a complex sugar called glycogen in the bodys cells. When a child inherits a pair of altered genes from 2 parents who are carriers as described above the result is decreased or absent levels of the GAA enzyme. The GAA gene is responsible for making this enzyme. Autosomal recessive disorders are genetic diseases which occur only when a.
































Post a Comment for "What Organelle Does Pompe Disease Affect In The Cell"