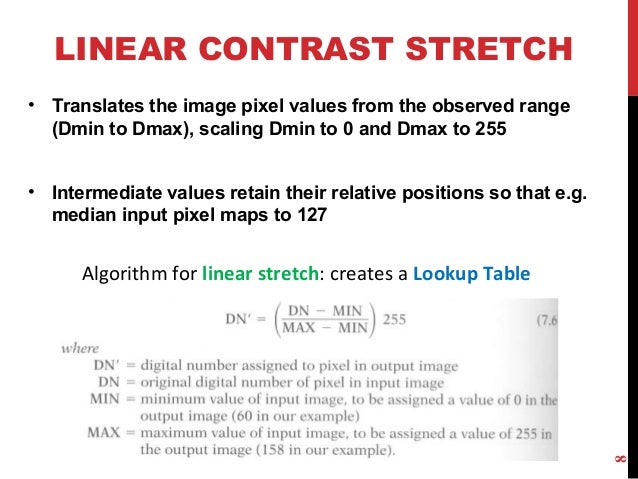
Contrast Stretching Example
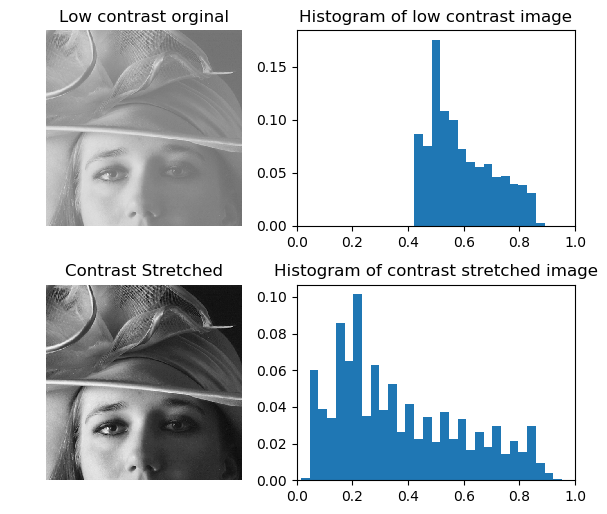
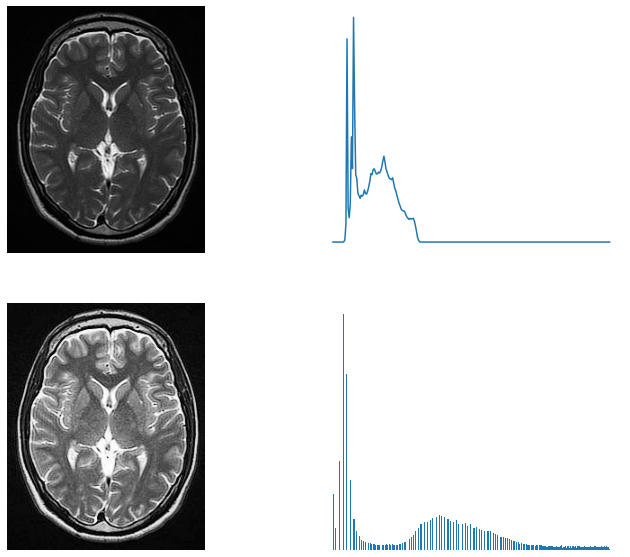
Contrast stretching example. The histogram of a low contrast image is usually skewed either to the left mostly light to the right mostly dark or located around the right mostly gray. Contrast stretching is also known as normalization. Now we calculate contrast from this image.
Improving Object Detection with Contrast Stretching Part 22 In the previous article about contrast stretching we explored percentile contrast stretching and how to apply this to obtain better performance in object detection models. The the full range of pixel values that the image type concerned allows. In image processing normalization is a process that changes the range of pixel intensity values.
To perform the stretching we have to specify the upper and lower pixel value limits over which the image is about to be normalized. There are a variety of other contrast stretch types. An image of low contrast has a small difference between its dark and light pixel values.
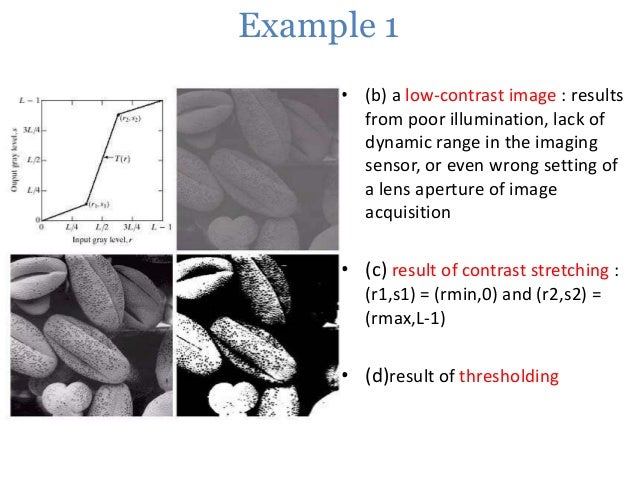
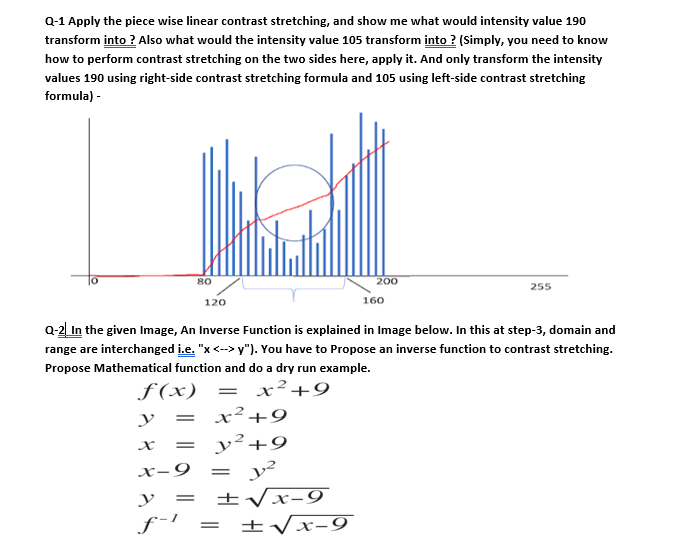
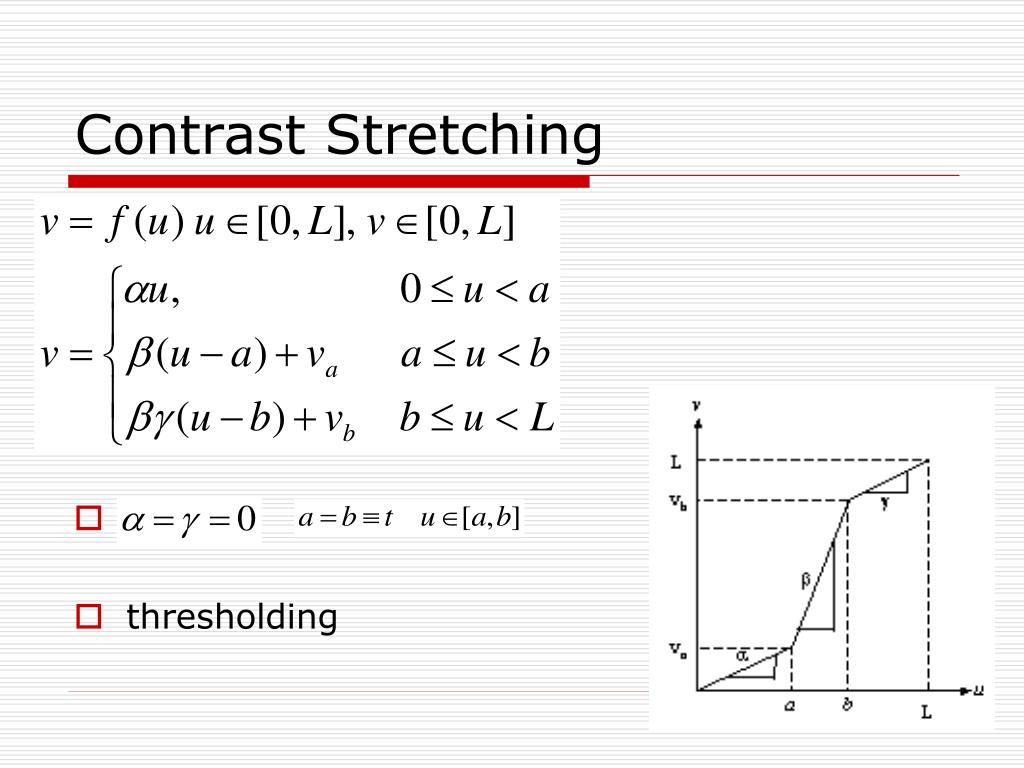
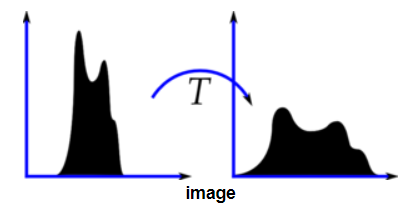
The figure below shows a typical transformation used for contrast stretching. Increasing the contrast of the image. Contrast modification in digital images is a point process that involves application addition subtraction multiplication or division of an identical constant value to every pixel in the image.
By changing the location of points r1 s1 and r2 s2 we can control the shape of the transformation. Logarithmic Transformations can be used to brighten the intensities of an image like the Gamma Transformation where gamma 1. The formula requires finding the minimum and maximum pixel intensity multiply by levels of gray.
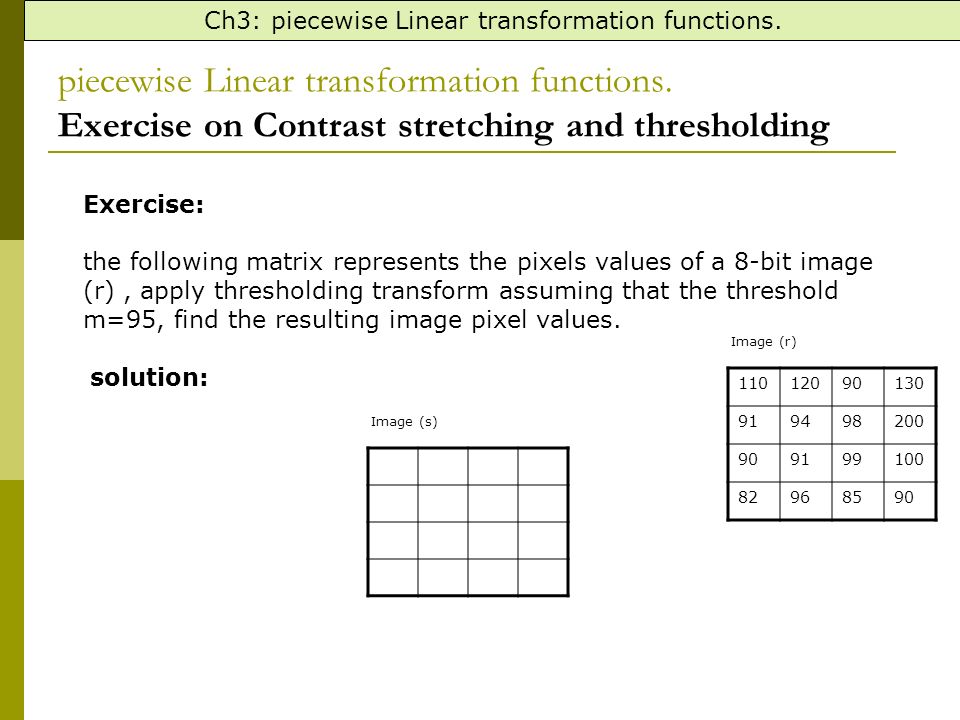
Lab 1. It is a simple image enhancement technique. Contrast stretching is a linear operation which means the value of the new pixel linearly varies based on the value of original pixel.
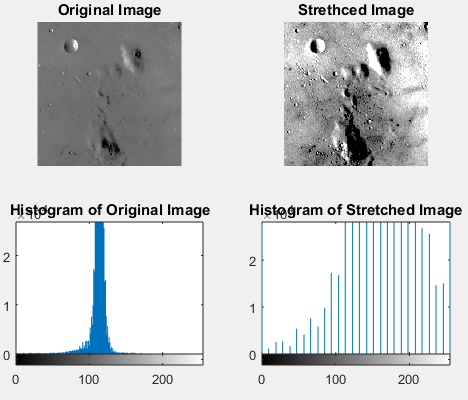
Unstretched TM B5 Image Linear stretched Image Linear Stretching Example A more efficient stretch would be one that mapped the range 40-110 to 0-255. Contrast stretching Normalization Brief Description.
Contrast Stretching and Histogram Normalization.
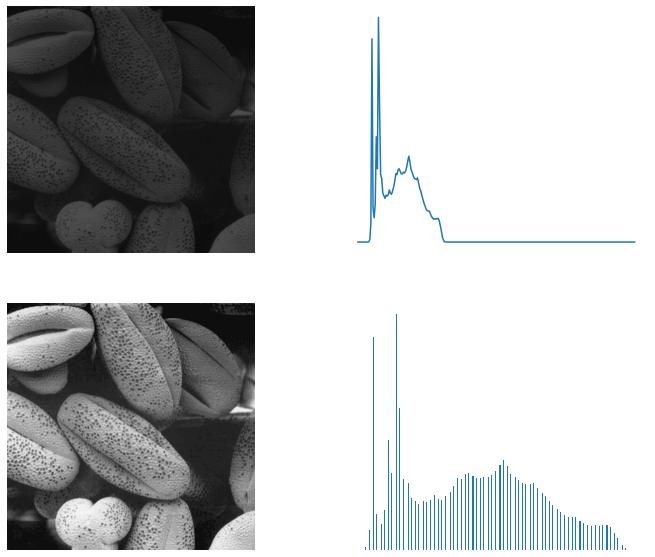
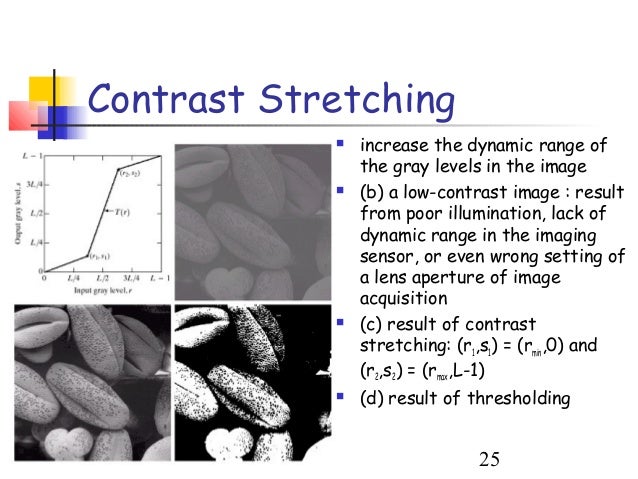
The histogram of a low contrast image is usually skewed either to the left mostly light to the right mostly dark or located around the right mostly gray. Below figure shows a typical transformation function used for Contrast Stretching. Percentile contrast stretching is also called histogram normalization as we normalize the range of the pixel intensities. There are a variety of other contrast stretch types. Contrast stretching of color images is not a trivial generalization of what is discussed for scalar images. For example all the pixels having values 1 will be replaced by 0 and all pixels having values 4 will be replaced by 1. The quality of image is enhanced by stretching the range of intensity values. Now we calculate contrast from this image. The the full range of pixel values that the image type concerned allows.
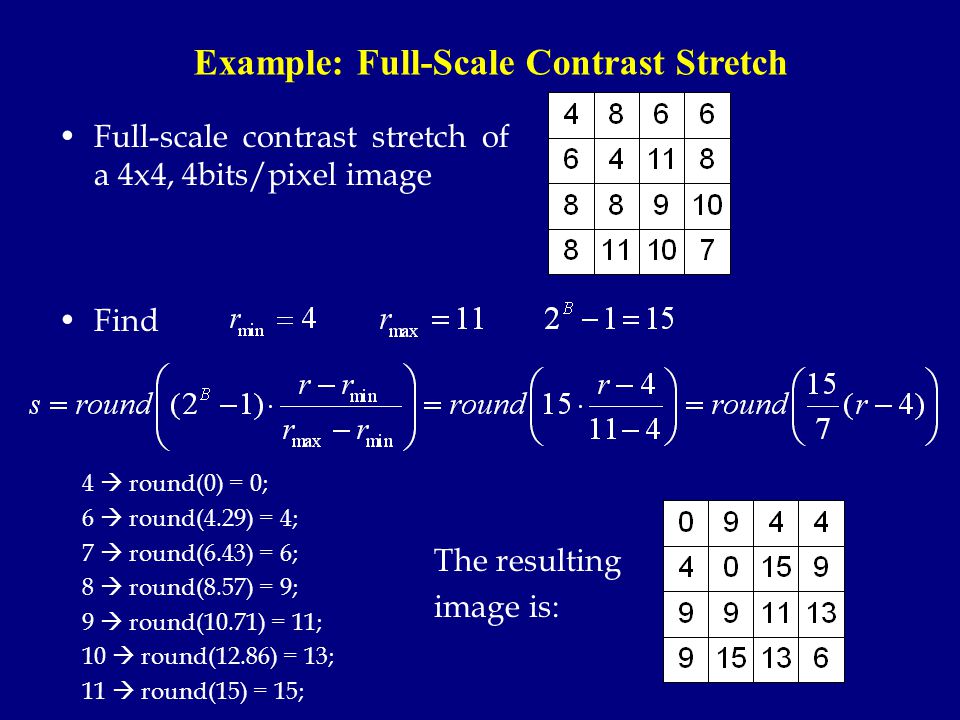
Contrast stretching of an image modifies the pixel values of the image in such a way that the intensities are transformed into a bigger range. This tutorial explores how redistributing brightness values through application of contrast. In more general fields of data processing such as digital signal processing it is referred to as dynamic range expansion. The formula requires finding the minimum and maximum pixel intensity multiply by levels of gray. And then stretch the contrast in the V image and use the new V. It is a simple image enhancement technique. The formula for stretching the histogram of the image to increase the contrast is.


























Post a Comment for "Contrast Stretching Example"